(a) Example of an Open Loop System:
In order to explain the open loop system we take the example of an automatic toaster. The block diagram of the toaster is shown in Figure.
The quality of the toast [bread slice] depends on the time for which the toaster is heated. Calibrated relays control the system. They control the heating time of the toast in the toaster. Relays are operated from external power source. They are adjusted by the calibrated dial to a particular time for the desired quality of the toast. The toaster heaters are energized after putting the toaster inside the heating chambers. Depending on the relay setting either the toasts are thrown out of the toaster or the toast is put off after the set interval of time.
The quality of the toast is to be judged by user. He will know it only after the toast is released out of the toaster. As the user is not a part of the system this system is called open loop system. The system input is also ineffective to disturbance produced in the toaster due to loss of addition of heat from surroundings.
(b) Practical Closed Loop System:
An automatic toaster with feedback is taken as an example of the practical closed loop control system. The block diagram is shown in Figure. The input of the system is desired quality of the toast. The output of the system is the actual quality of the toast. The actual toast quality in the toaster is measured by a quality measuring device like a colour detector placed in the toaster.
It produces a signal proportional to toast quality. This quality is then compared with the desired toast quality to generate an error signal. This error signal is detected by the controller that changes the heating time. The heating time is changed through relays such that the error is reduced. This makes the actual toast quality same as desired one.
The disturbance in the toaster due to temperature changes from surrounding conditions change the toast quality. This is because the toast heating intensity is changed. It is to be noted that the quality is important here. It is very important compared with the desired toast quality.
The disturbances are also transmitted to the comparator, through the feedback path. They also influence the error. Thus in this system the input is influenced by the output and disturbances through the feed back path.
In order to explain the open loop system we take the example of an automatic toaster. The block diagram of the toaster is shown in Figure.
 |
Block Diagram of a Toaster |
The quality of the toast is to be judged by user. He will know it only after the toast is released out of the toaster. As the user is not a part of the system this system is called open loop system. The system input is also ineffective to disturbance produced in the toaster due to loss of addition of heat from surroundings.
(b) Practical Closed Loop System:
An automatic toaster with feedback is taken as an example of the practical closed loop control system. The block diagram is shown in Figure. The input of the system is desired quality of the toast. The output of the system is the actual quality of the toast. The actual toast quality in the toaster is measured by a quality measuring device like a colour detector placed in the toaster.
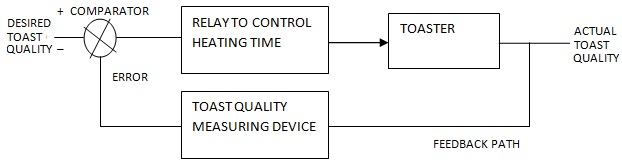 |
| Automatic Toaster with Closed Loop Control |
The disturbance in the toaster due to temperature changes from surrounding conditions change the toast quality. This is because the toast heating intensity is changed. It is to be noted that the quality is important here. It is very important compared with the desired toast quality.
The disturbances are also transmitted to the comparator, through the feedback path. They also influence the error. Thus in this system the input is influenced by the output and disturbances through the feed back path.
Tags:
Instrumentation
